Geography Curriculum
1. What’s it for?
It enables students:
(a) to use geographical concepts and knowledge to understand real problems at local, national and global scales;
(b) to master geographical skills, enquiry skills and generic skills; and
(c) to develop their interest in and concern about environmental change, impact and management.
2. What to learn?
(a) The junior secondary geography curriculum
The three-year junior secondary geography curriculum covers the following modules. In each module, students are involved in enquiry about the issues in local, national and/or global contexts.
Modules covered | |
One | Using urban space wisely |
Two | The trouble with water Food problem Taming the sand |
Three | Living with natural hazards Changing climate, changing environment |
The curriculum is also tailored to equip junior form students with basic geographical concepts (including space, place, region, and human-environment interaction), enquiry and generic skills, and map reading skills which are essential for their further study.
(b) The senior secondary geography curriculum
The geography curriculum consists of the Compulsory Part and Elective Part. Two electives are chosen according to students’ abilities, needs and interests. In the course of study, students’ conceptual understanding and higher-order thinking skills, such as critical thinking skills, problem-solving skills and creativity are further developed for their university study.
In all forms, values for sustainable living, including those of social responsibility, care for others, respect for others and commitment to work with others and for others are infused into the curriculum.
- How do teachers teach and students learn?
To make learning more meaningful, teachers prepare tasks for students to process lesson content actively, design group activities to stimulate their development of multiple perspectives and connect students’ learning to their real-life experiences during the lessons inside and outside the classrooms.
Features of teaching and learning geography:
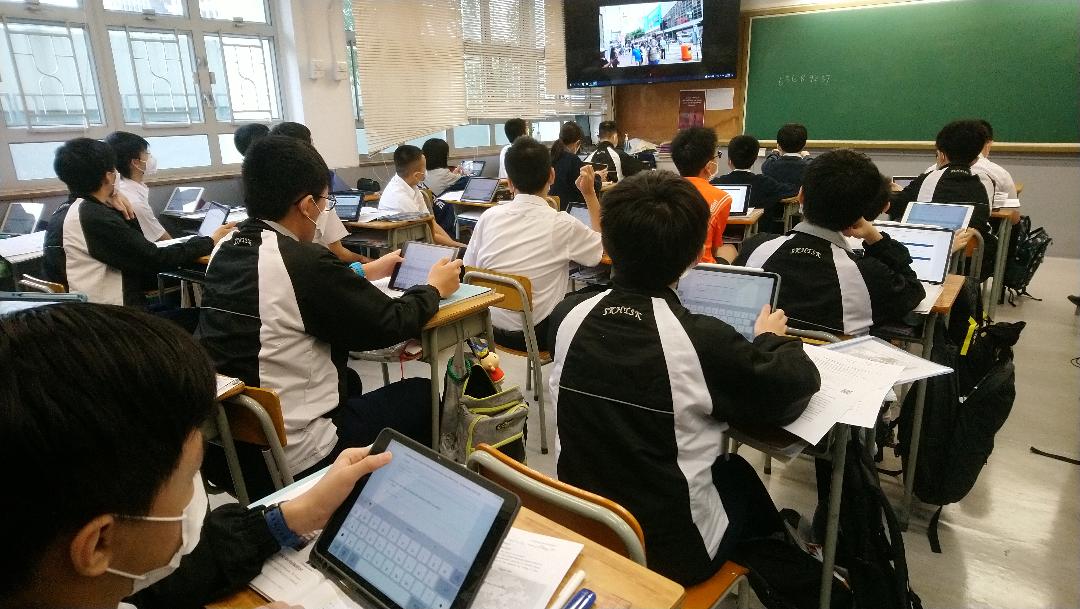
(a) Using information technology (IT) in geography
E-learning is widely adopted in geography. Apart from using IT as a presentation tool, some educational apps are employed to conduct interactive activities and game-based activities in the lessons. Regarding some topics, 360o street view images, VR photos and AR images are used to help students conceptualize some abstract knowledge or to be the sources of data for enquiry learning. What's more, e-assessment tasks are set in the eClass for instant feedback. To extend the learning time, extra resource materials like current news and videos are uploaded to help senior form students learn beyond the lessons at their own pace.

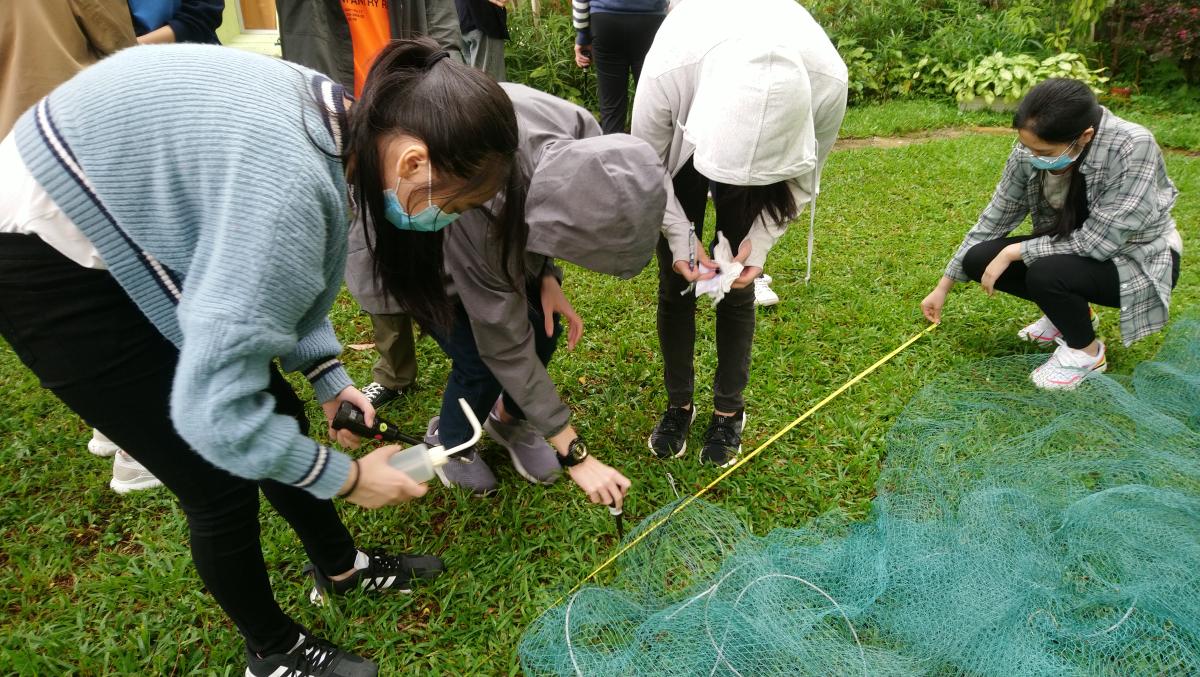
(b) Teaching and learning through fieldwork
In junior forms, fieldwork enquiry tasks are designed to help students to apply the knowledge and concepts learnt and practise some basic fieldwork skills in real situations or on virtual field trips using Google Earth.
Form | Modules | Topics for enquiry fieldwork |
One | Using urban space wisely | Urban renewal in Wanchai |
Two | Food problem | Farming in the local context |
Three | Living with natural hazards | Preventive measures of landslides |
In senior forms, students are arranged to join the field study courses mainly organized by the two field study centres in which they go through different processes in the fieldwork enquiry. The topics chosen for field study mostly depend on what modules are selected for setting fieldwork-based questions by the HKEAA in each cohort.

(c) Learning geography through case studies
In F.2-4, students are assigned to have case studies about different types of natural hazards that they have learnt about. In each form, they have to work in groups, choose recent cases for study, search for the relevant materials, organize the information and write up the reports according to the outlines provided.
Form | Modules covered | Topics for Case studies |
Two | The trouble with water | Floodings / droughts |
Three | Living with natural hazards | Earthquakes |
Four | Opportunities and risks | Tsunamis |
(d) Promotion of reading to learn
To broaden or deepen students’ knowledge, junior form students are assigned to read extra materials that are suited to their linguistic skills. Geographical questions relating to the texts are set to check students’ understanding in the follow-up activities.
(e) Adopting the ‘Language-across-the-curriculum’ (LaC) approach
To facilitate junior form students to learn the geographical content in English effectively, they are guided to read and write in the geography worksheets from vocabulary, and then sentence to paragraph levels.
(f) Providing learning opportunities for talented students
To help F.4-5 high-achievers excel in their talented area, a one-year ‘Web-based Learning Course for the Gifted / More Able Students’ within the domain of Earth Science is offered by the Hong Kong Academy for Gifted Education and the Education Bureau every year.